Introduction
Understanding Sciatica
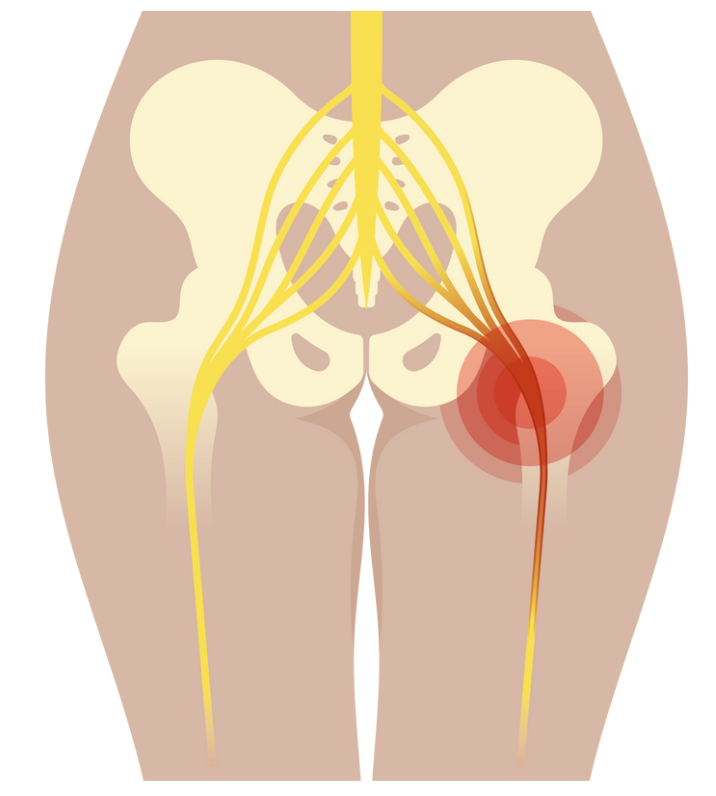
Sciatica refers to the pain associated with the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back through the hips and buttocks and down each leg. Understanding the condition's anatomy, causes, and impact is crucial for effective management.
Definition, Symptoms, and Anatomy
Sciatica is characterized by pain radiating along the sciatic nerve, the longest and widest nerve in the human body. Symptoms can include pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the lower back, buttock, leg, and foot on one side of the body. The term "sciatica" comes from the Greek word "iskhiadikos," meaning "hip pain," reflecting its common presentation in the lower back and leg areas.
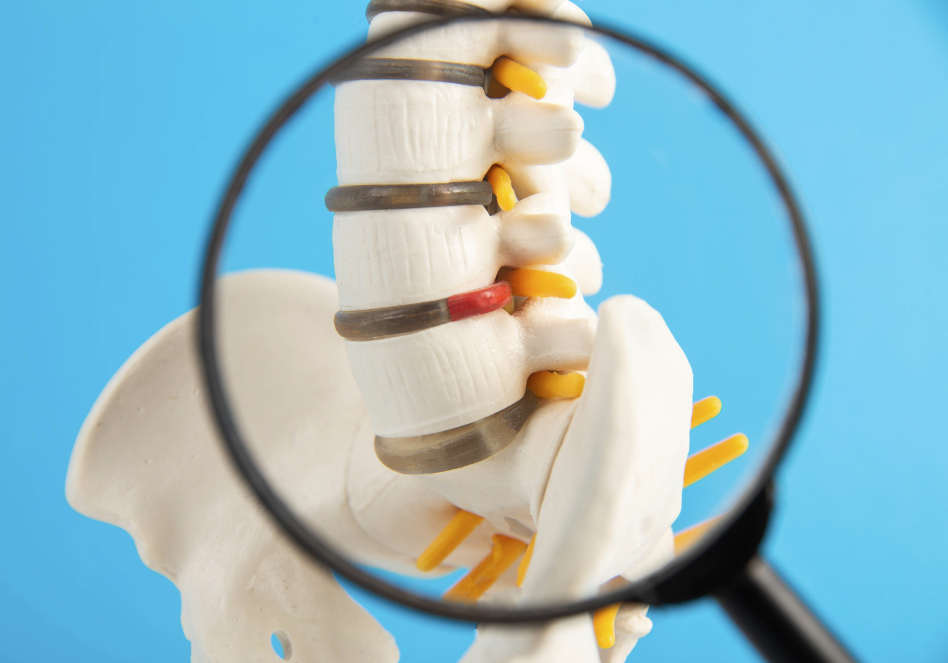
The sciatic nerve originates from the nerve roots in the lumbar spine (L4 to S3) and travels through the pelvis, under the piriformis muscle, then descends through the hamstrings in the thigh. It branches out at the knee, extending through the calf muscles and further dividing into smaller nerves that reach the foot and toes. Common compression points include the lumbar vertebrae, where the nerve roots exit the spinal column and the pathway through the piriformis muscle.
Physiology and Pathology
In healthy individuals, the sciatic nerve facilitates leg movement and sensation. Sciatica develops when the nerve is compressed, often by a herniated disc or bone spur, leading to inflammation and pain.
Causes of Sciatica
Sciatica can result from spinal disorders like herniated discs, lumbar spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, herniated discs are the most common cause of sciatica. In the United States, sciatica affects around 10 to 40 percent of the population at some point in their lives, translating to millions of people experiencing this condition annually.
Recovery Time
The duration of sciatica symptoms can vary. Without intervention, symptoms may persist for weeks to months. However, with appropriate physical therapy and exercise, many patients see significant improvement within 4 to 6 weeks. This faster recovery timeframe is supported by clinical evidence showing that targeted exercises can effectively reduce sciatic nerve compression and alleviate symptoms.
Understanding the detailed anatomy and common causes of sciatica, along with effective treatment and recovery timelines, is essential for anyone seeking to manage this condition and improve their quality of life.
Diagnosing Sciatica
Diagnosing sciatica involves a comprehensive evaluation to differentiate it from other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. The process typically includes:
- A medical history review.
- Physical examination.
- Diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of sciatic nerve irritation and identify its cause.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing sciatica is a thorough medical history review, where the healthcare provider will ask about the nature, duration, and severity of the symptoms, as well as any activities or behaviors that alleviate or exacerbate the pain. The doctor will assess spinal movements, leg strength, reflexes, and sensation during the physical examination. Tests like the straight leg raise (SLR) test are commonly used to evaluate sciatic nerve irritation, where lifting the leg while lying down stretches the sciatic nerve and can reproduce sciatica symptoms.
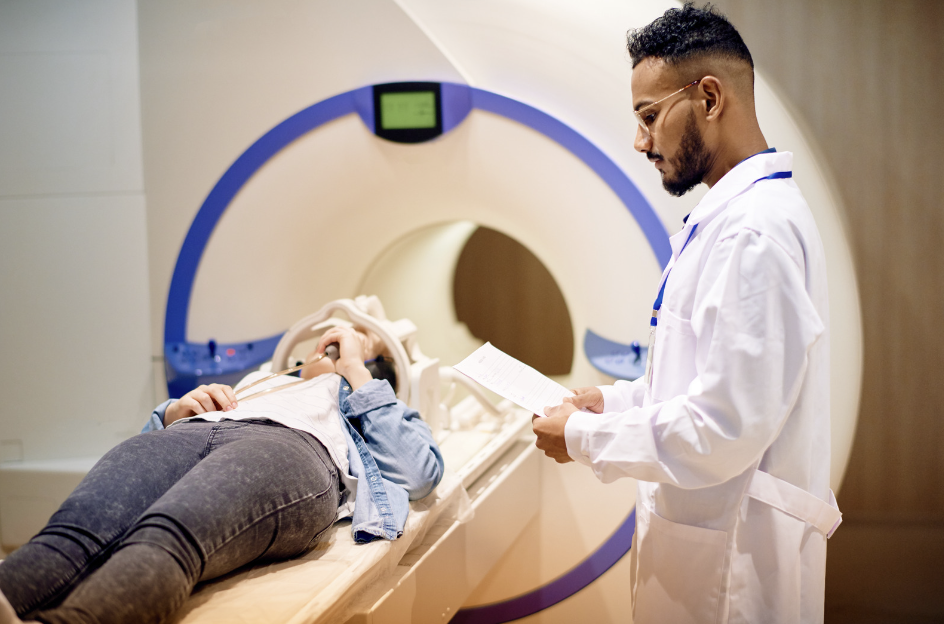
Diagnostic Imaging
If the physical examination suggests sciatica, the doctor may order diagnostic imaging tests to identify the underlying cause of the nerve compression. Standard imaging tests include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of the body's soft tissues, including the spinal cord, nerve roots, and intervertebral discs, helping to pinpoint herniated discs or other abnormalities that may be pressing on the sciatic nerve.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan:
When MRI is unavailable or contraindicated, a CT scan combined with a myelogram (injecting contrast dye into the spinal column) can provide detailed images of the spinal structure and identify issues affecting the sciatic nerve.
- X-rays: While not as detailed for soft tissue structures, X-rays can show spinal alignment and reveal bone spurs or other skeletal causes of sciatica.
Accurate diagnosis of sciatica is crucial for determining the most effective treatment plan. By identifying the specific cause of sciatic nerve compression, healthcare providers can tailor treatment strategies to address the root of the problem, potentially alleviating symptoms and improving function.
Managing and Treating Sciatica
Effective management and treatment of sciatica integrate medical interventions, physical therapy, strength training, and lifestyle modifications to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and enhance mobility.
Medical Treatments
Treatment options for sciatica may include:
- Medications: Pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can ease pain and inflammation. For more intense pain, prescription medications such as muscle relaxants or anti-inflammatories may be necessary.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored physical therapy programs focus on strengthening spine-supporting muscles, increasing flexibility, and improving posture to mitigate sciatic pain.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation around the nerve root, offering pain relief.
- Surgery: If conservative treatments fail and significant nerve compression is present, surgery might be considered to alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve.
Exercise and Physical Activity
A comprehensive approach to physical activity is crucial in managing sciatica:
- Strength Training: Incorporating strength exercises to bolster the muscles around the spine and pelvis can enhance support for the back, alleviating pressure on the sciatic nerve.
- Stretching: Flexibility exercises for the back and leg muscles can improve the range of motion and reduce nerve tension.
- Core Strengthening: Building core stability supports the spine, reducing the burden on the sciatic nerve.
- Low-Impact Aerobic Activities: Walking or swimming can boost cardiovascular health and spinal fitness without excessive strain on the back.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adapting lifestyle habits can significantly aid in the management and prevention of sciatica:
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Creating an ergonomic working environment can help maintain proper posture and decrease lower back stress.
- Weight Management: Keeping a healthy weight reduces spinal and lower extremity strain.
- Posture Correction: Consistent attention to good posture during sitting, standing, and movement relieves pressure on the sciatic nerve.
Managing and treating sciatica effectively entails a multidimensional strategy that addresses pain relief, improves physical function, and prevents future episodes. Individuals can significantly alleviate sciatica symptoms and enhance their well-being by combining medical treatment with strength training, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Royal Blue Fitness: Specialized Support for Sciatica Management
At Royal Blue Fitness, we provide:
- Specialized support for individuals suffering from sciatica.
- Emphasizing our deep understanding of anatomy.
- Sophisticated programming.
- Meticulous attention to detail.
Our approach is rooted in a comprehensive analysis of each client's condition, ensuring a tailored program to address their unique needs and alleviate pain effectively.
Expertise in Anatomy and Physiology
Our team's anatomy and physiology expertise enables us to accurately identify the underlying causes of sciatic pain. We thoroughly understand the sciatic nerve's pathway and how various factors can lead to nerve compression and irritation. This knowledge is crucial for designing targeted exercise programs that relieve and facilitate recovery.
Sophisticated Programming
We employ sophisticated programming that blends strength training, flexibility exercises, and core stabilization. These exercises are all aimed at supporting the spine and reducing pressure on the sciatic nerve. Our programs are customized to meet our client's needs and health goals, ensuring a focused and practical approach to pain relief and functional improvement.
Attention to Detail
Our meticulous attention to detail ensures that each exercise is performed with proper form and intensity, avoiding further irritation of the sciatic nerve. We also closely monitor client progress, making adjustments as necessary to promote continuous improvement and avoid potential setbacks.
Royal Blue Fitness is a reliable stalwart for those seeking to overcome sciatica and regain a pain-free, active lifestyle. Through our expertise, tailored programming, and detail-oriented approach, we provide the support and guidance necessary for effective sciatica management and recovery.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively managing sciatica is crucial for maintaining a high quality of life and minimizing the impact of this common nerve-related pain condition. Individuals can significantly alleviate sciatica symptoms and enhance their overall well-being with the right approach, including medical treatment, physical therapy, strength training, and lifestyle changes.
Royal Blue Fitness is a stalwart pillar of reliability in overcoming sciatica. With our personalized programs, deep anatomical knowledge, and commitment to each client's health, we offer a path to a pain-free, active lifestyle. Our dedication to quality and detail ensures that every client receives the care and guidance needed to manage their sciatica effectively and achieve lasting relief.
Resources for Further Reading
For those seeking more information on sciatica, its causes, and management strategies, the following resources offer valuable insights:
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS): Provides detailed information on the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of sciatica.
AAOS Sciatica
Resource
- Johns Hopkins Medicine: Offers expert insights into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sciatica.
Johns Hopkins Medicine Sciatica Page
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS): Contains research and educational material on sciatica, including symptom management and therapy options.
NINDS Sciatica Information
- WebMD: Presents an overview of sciatica, covering causes, symptoms, and treatments.
WebMD Sciatica Overview
These resources can provide further knowledge and understanding of sciatica, aiding individuals in navigating their condition and seeking the most effective treatments.