Breaking the Cycle: Effective Strategies for Sustainable Weight Loss
Introduction: The Weight of Obesity
Obesity is not just a personal challenge; it is a global health crisis that continues to grow. Characterized by an excessive accumulation of body fat, obesity significantly heightens the risk of numerous health issues. It is a leading cause of preventable death worldwide. This condition has reached epidemic proportions in many countries, affecting adults and children alike and posing complex challenges to health systems globally. Addressing this crisis requires evidence-based approaches and sustainable weight loss strategies that promote long-term health and behavior change.
In the United States, the statistics are particularly alarming. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the prevalence of obesity was over 42% in recent years. This high rate of obesity brings with it an increased burden of medical conditions, including type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, and various musculoskeletal disorders, particularly osteoarthritis. The economic impact is also significant, with billions of dollars spent annually on medical costs associated with obesity.
Beyond the physical health risks, obesity severely affects an individual’s quality of life. It can impair mobility, reduce life expectancy, and lead to psychological issues such as depression and low self-esteem. The stigma associated with obesity can further exacerbate mental health struggles, creating a cycle that can be difficult to break.
Addressing obesity is crucial not only to reduce the prevalence of related health complications but also to enhance overall societal health and reduce healthcare costs. It requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and community and societal support. This article explores effective sustainable weight loss strategies, emphasizing the crucial roles of exercise, diet, and behavioral changes. By adopting a holistic approach, individuals can achieve significant health improvements and a higher quality of life, breaking the cycle of obesity and its associated challenges.

Understanding Obesity
Definition and Causes
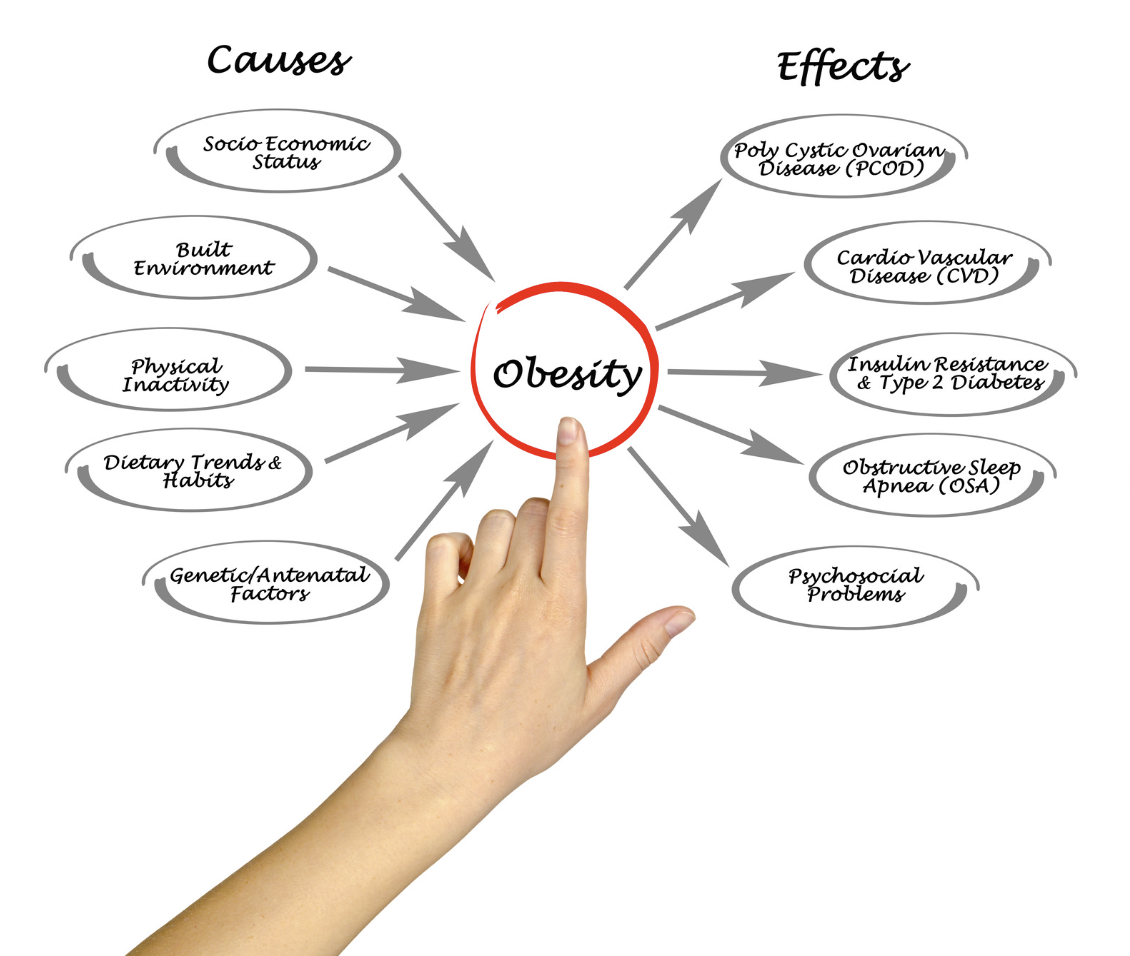
Obesity is medically defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. BMI is a simple index of weight-for-height that is commonly used to classify overweight and obesity in adults. The condition develops from an energy imbalance—consuming more calories than are expended through physical activity and daily life functions. However, the causes of obesity are multifaceted and extend beyond calorie intake and exercise levels:
- Genetic Factors: Genetics can significantly affect how an individual's body processes food and stores fat. People with a family history of obesity may have a higher genetic predisposition to the condition.
- Environmental Factors: One's environment significantly impacts dietary habits and opportunities for physical activity. For example, easy access to high-calorie foods and limited access to safe places to work out contribute to the obesity epidemic.
- Lifestyle Choices: Sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy diets, and inadequate physical activity are major contributors to obesity. Behavioral patterns established over time can only change with targeted interventions.
Health Risks
The health risks associated with obesity are numerous and can be severe:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Obesity is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. Excess body fat leads to increased cholesterol, triglycerides, and high blood pressure and can induce diabetes, which strains the cardiovascular system.
- Diabetes: Obesity is a leading cause of type 2 diabetes. Excess fatty tissue leads to increased resistance to insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels.
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: The excess weight associated with obesity puts tremendous strain on bones and joints, leading to conditions such as osteoarthritis.
- Cancer: There are several types of cancer linked to obesity, including breast, colon, and kidney cancers.
Psychological Impacts
The impact of obesity is not limited to physical health; it also carries significant psychological consequences:
- Stigma and Discrimination: Individuals with obesity often face social stigma and discrimination, which can affect their education, employment, and social interactions.
- Mental Health Issues: The psychological stress of living with obesity can lead to depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. The emotional distress associated with obesity can also contribute to unhealthy eating patterns, further complicating the issue.
- Quality of Life: Obesity can restrict physical activity, limit mobility, and impact the overall quality of life. It can inhibit daily activities and personal independence, affecting an individual's ability to engage with their community and lead an active life.
Understanding these factors is crucial for addressing obesity effectively. Recognizing the causes and consequences of obesity helps develop personalized approaches for managing and reversing the condition. Individuals can achieve sustainable weight management and improve their overall health through comprehensive strategies that address diet, exercise, and psychological support.
The Role of Exercise in Obesity Management in Pleasant Hill
Exercise Guidelines and Intensity
Managing obesity effectively requires adherence to established exercise guidelines promoting safety and effectiveness. According to the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM), individuals with obesity should aim for at least 150 to 250 minutes per week of moderate-intensity physical activity to prevent weight gain and achieve modest weight loss. More than 250 minutes per week is recommended for more significant sustainable weight loss strategies. Moderate-intensity activities, such as brisk walking or cycling, elevate the heart rate and breathing but still allow one to hold a conversation.
Engaging Training Modalities
Engagement and enjoyment in exercise are crucial for long-term adherence. Here are a few training modalities that can make the exercise experience more enjoyable and engaging:
- Group Fitness Classes: Participating in Zumba, spin, or water aerobics classes can provide a supportive and fun environment.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): For those with limited time, HIIT involves short bursts of intense activity followed by rest or lower-intensity periods. It's efficient and can be more engaging than steady-state cardio.
- Strength Training: Incorporating resistance training such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises helps build muscle, boost metabolism, and change body composition.
Incorporating Exercise into Daily Life
Starting an exercise routine can be daunting, especially for those concerned about judgment or feeling out of place. Here are tips for easing into a physically active lifestyle:
- Start Slowly: Begin with manageable amounts of exercise and gradually increase the duration and intensity as confidence and stamina build.
- Set Realistic Goals: Setting achievable goals can help maintain motivation and provide a sense of accomplishment that encourages further effort.
- Find Enjoyable Activities: Choose forms of exercise that you enjoy. Enjoyment is a powerful motivator and can make the routine less of a chore and more of a fun part of the day.
- Create a Support Network: Engaging friends or family or joining a group can provide encouragement and accountability, which are key for maintaining an exercise routine.
Overcoming Barriers and Enhancing Motivation
Exercise can significantly enhance mood and boost energy levels, creating a positive feedback loop that motivates further activity:
- Mood Enhancement: Regular physical activity can reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, often known as the body's natural mood elevators.
- Energy Boost: As physical fitness improves, so does energy efficiency. Regular exercisers often report higher levels of vigor and less fatigue, making it easier to maintain an active lifestyle.
Professional Guidance and Support
While personal motivation is important, professional guidance can dramatically enhance the effectiveness of exercise routines:
- Exercise Professionals: Certified fitness trainers or exercise physiologists can tailor workouts to individual needs, maximizing benefits and minimizing the risk of injury.
- Routine Assessments: Regular check-ins with a professional can help adjust exercise plans as fitness levels improve or as goals change.
Transitioning into a more active lifestyle requires initial change and ongoing adjustments and support. By understanding these elements and gradually incorporating them into daily life, individuals can transform their approach to exercise and take significant strides in managing obesity.

Nutritional Strategies for Managing Obesity
Balanced Diet Principles
A balanced diet is essential for managing obesity and fostering overall health improvement. It involves reducing calorie intake and ensuring that those calories are nutrient-dense and support metabolic health.
- Diversity in Diet: Incorporating a variety of food groups ensures a wide range of necessary nutrients. Each meal should include a balance of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats—as well as essential vitamins and minerals from fruits and vegetables.
- Consistent Nutrient Intake: Regular, balanced meals help regulate blood sugar levels, reduce cravings, and prevent binge eating.
Specific Dietary Recommendations
Managing dietary intake is crucial for effective weight management:
- Foods to Include: Focus on whole foods, such as vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats like those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil. These foods are nourishing and help you feel fuller for longer, which can aid in weight loss.
- Foods to Avoid: Minimize intake of high-calorie, low-nutrient foods such as processed snacks, sugary beverages, and high-fat fast foods. These contribute to calorie excess and poor health outcomes.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day aids digestion, helps fill the stomach, and improves metabolism, all of which are beneficial for weight management.
Role of Portion Control and Meal Planning
Controlling portion sizes and planning meals are effective strategies for managing weight:
- Portion Control: Understanding and adhering to recommended serving sizes can prevent overeating. Tools like measuring cups or scales can help until you're comfortable estimating portion sizes visually.
- Meal Planning: Planning meals can prevent last-minute choices that often result in less nutritious meals. It helps maintain a balanced diet and can also be cost-effective and time-saving.
Creating a Supportive Network
Developing a support network is vital for sustained weight management success:
- Family and Friends: Engage family members or friends in your health journey. Sharing meals or exercising together can make these activities more enjoyable and reinforce your commitment.
- Professional Support: Dietitians and nutritionists can provide professional advice tailored to your specific needs. Their expertise can help you navigate challenges and adjust your diet as needed.
- Online and Community Resources: Joining online forums or local groups focused on healthy living can provide encouragement and motivation. Learning from others' experiences and sharing your own can foster a sense of community and accountability.
Implementing these nutritional strategies requires commitment and consistency but can significantly impact weight management and overall health. By combining balanced dietary practices with a supportive environment, individuals with obesity can make lasting changes that reduce weight and enhance their quality of life.

The Importance of Behavior Change
Building Healthy Habits
Creating sustainable weight management begins with establishing consistent, health-promoting habits:
- Set Clear Goals: Define specific, measurable, and realistic goals that guide daily actions, whether incorporating more vegetables into your diet or walking 10,000 steps a day.
- Routine Formation: Anchor your new habits in daily routines, such as planning workouts at the same time each day or preparing healthy meals in advance. Consistency turns actions into habits.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward yourself for milestones to reinforce progress, choosing rewards that complement your health goals, such as a wellness retreat or a new exercise outfit.
Overcoming Challenges
The journey to sustainable weight loss is fraught with challenges that can derail progress:
- Plateaus: Weight loss plateaus can be frustrating. Address them by revising your diet and exercise plan or consulting a health professional to reassess your strategies.
- Social Situations: Navigate social gatherings by planning, such as eating a healthy snack before events or choosing lighter meal options available.
- Emotional Eating: Identify emotional triggers that lead to overeating. Develop healthier coping mechanisms, such as engaging in physical activity or using relaxation techniques.
- Lack of Support: Cultivate a support system that understands and supports your health goals. Clear communication about your needs can help you receive the encouragement necessary to persist.
- Persistence: It is challenging to stay motivated over the long term. Remind yourself of the benefits you've gained from your healthier lifestyle and the importance of maintaining these changes.
Maintaining Progress for Sustained Success
Achieving your weight goal is an important milestone, but maintaining weight loss is often more challenging. Transitioning from weight loss to weight maintenance requires adjusting both your mindset and applying sustainable weight loss strategies.
- Lifestyle Integration: Integrate healthy habits into your lifestyle permanently rather than viewing them as temporary changes. This includes continuing to eat well, exercising regularly, and managing stress.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of your weight and body composition regularly to catch any changes early. Regular check-ins with a health professional can provide guidance and adjust your plan as needed.
- Continuous Learning: Stay informed about the latest health and nutrition research that can provide new insights and techniques to enhance your health strategy.
- Social Engagement: Participate in community fitness events or online forums to stay motivated and connected with others focused on maintaining healthy lifestyles.
- Adaptability: Be prepared to adapt your health strategies as your body and circumstances change. Flexibility can help you maintain progress and manage any new health challenges effectively.
By focusing on these strategies, you can ensure that your progress is durable and that your journey towards health continues to evolve and enrich your life. This approach not only helps maintain the weight loss achieved but also promotes an ongoing, vibrant health status that supports a fulfilling life.

Royal Blue Fitness's Holistic Approach
At Royal Blue Fitness, we understand that tackling obesity is a sensitive and complex challenge. Our approach is built on empathy, expertise, and a commitment to providing a supportive environment where clients feel valued and understood. We recognize that each journey to weight management is unique, and we are dedicated to helping clients achieve their health goals in a judgment-free zone.
Comprehensive Weight Management Program
Our comprehensive weight management program is designed to address all aspects of effective weight loss and long-term management:
- Fitness Training: We offer a wide range of exercise options tailored to meet each client's fitness levels and preferences. Whether it's group classes that offer motivation and community support or one-on-one sessions with a personal trainer for focused guidance, our programs are designed to make physical activity enjoyable and effective.
- Nutritional Counseling: Nutrition is a cornerstone of effective weight management. Our certified nutritionists work closely with clients to create personalized eating plans that promote sustainable weight loss. These plans are about reducing calorie intake and ensuring a balanced and nutritious diet that supports overall health and well-being.
- Psychological Support: We acknowledge the psychological challenges associated with weight loss. Our approach includes supporting emotional eating, building a positive body image, and developing a healthier relationship with food. We provide resources and support for mental wellness to help clients navigate the emotional aspects of their weight loss journey.
Customized Support
Understanding that each individual has unique needs and challenges, we emphasize the personalized nature of our programs:
- Tailored to Individual Needs: From the outset, we conduct thorough assessments to understand each client's health status, fitness level, and personal goals. This information is used to tailor every aspect of the program, from workout routines to dietary plans.
- Adaptive Strategies: As clients progress on their journey, their needs may change. Our team is agile, making necessary adjustments to the program to ensure it remains effective and aligned with the client's evolving goals.
- Continuous Guidance: Our experts are with you every step of the way, providing guidance, encouragement, and accountability. We help clients overcome obstacles and celebrate their successes, making the journey to better health a collaborative and supportive experience.
Royal Blue Fitness is more than just a gym; it's a community committed to empowering individuals to take control of their health and achieve lasting weight management success. By combining expert knowledge with a compassionate approach, we help our clients reach their weight goals and enhance their overall quality of life.

Conclusion: Empowering Change
As we conclude our exploration of effective strategies for managing obesity, it is clear that a holistic approach is essential. Obesity is not just a matter of excess weight; it is a multifaceted health issue that affects individuals physically, emotionally, and psychologically. Addressing weight management effectively requires more than just temporary diet plans or sporadic exercise—it demands a comprehensive and sustained effort encompassing all health aspects.
This article discusses the critical role of balanced nutrition, regular and varied physical activity, behavior change, and psychological support in combating obesity. These elements are interlinked, each vital in sustainable weight management. By adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity tailored to personal needs, and addressing psychological factors such as stress and emotional eating, individuals can significantly improve their health and quality of life.
Partnering with Royal Blue Fitness offers a unique advantage in this journey. Our holistic approach goes beyond standard weight loss programs by offering personalized, comprehensive support that addresses each individual's unique challenges and needs. At Royal Blue Fitness, clients receive tailored exercise programs, customized nutritional guidance, and continuous emotional and psychological support, all within a nurturing and nonjudgmental environment.
By working with Royal Blue Fitness, you are not just embarking on a weight loss journey; you are starting a transformative journey towards a healthier and more fulfilled life. We are committed to guiding you every step of the way, providing the tools and support needed to achieve and maintain your health goals. Together, we can break the cycle of obesity and empower you to lead a vibrant, healthier life.
Resources for Obesity and Weight Management
For further information, guidance, and tools on managing obesity and achieving sustainable weight loss, consider exploring these resources from reputable organizations:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Offers detailed guidance on healthy weight loss, including strategies for eating well and moving more. The CDC provides data on the prevalence of obesity in the U.S. and offers tools for tracking food and physical activity. VisitCDC
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: Offers a wealth of resources on managing obesity through lifestyle changes. Their site includes meal planning guides, tips on physical activity, and strategies to manage and prevent obesity. Visit NIH-NHLBI
- The Obesity Action Coalition (OAC): Provides comprehensive information on obesity, the risks associated with obesity, and various treatment options. The OAC also advocates for the rights of individuals struggling with weight and offers a community for support. VisitOAC
- The American Heart Association (AHA): Discusses the link between obesity and heart disease and offers practical advice on how to reduce risks through diet and exercise. The AHA also provides recipes, videos, and tools for better heart health. VisitAHA
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Features tips from registered dietitians on how to manage weight and eat well. Their resources include how to read nutrition labels, portion control guides, and nutritional strategies tailored to specific needs, such as managing diabetes or high blood pressure. VisitEatRight
These resources can help you gain a deeper understanding of obesity and provide practical tools and tips for obesity management in Pleasant Hill through lifestyle changes, nutrition, and exercise.