Cardiovascular Wellness: Integrating Exercise, Nutrition, and Stress Management
Introduction: Embracing a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Heart disease is a profound challenge that touches the lives of millions, with each heartbeat bringing worry for many about the potential impact of cardiovascular issues on their day-to-day life. This article is crafted with empathy and care, recognizing the daily struggles faced by those living with heart disease or the anxiety of those at risk.
Our goal is to provide a compassionate guide to understanding cardiovascular health. We detail cardiovascular disease, identify its risk factors, and explore effective strategies to combat it through lifestyle choices. Whether you're directly affected by heart conditions or concerned about future risks, this article aims to educate and empower you with knowledge and practical steps towards a healthier heart.
We will delve into the benefits of regular exercise, the importance of a balanced diet, and the role of stress management in maintaining cardiovascular health. By the end of this read, you'll have a clearer understanding of how integrated approaches involving fitness, nutrition, and emotional well-being can contribute to long-term heart health. This guide is designed to equip you with the tools to take proactive steps towards a heart-healthy lifestyle, fostering physical and emotional resilience.

Understanding Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular Disease Overview
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) encompasses a group of disorders affecting the heart and blood vessels, and it remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. To effectively combat this disease, it is crucial to understand its various forms, causes, and mechanisms affecting the body.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Involves reduced blood flow to the heart muscle due to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Heart Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms affecting how effectively the heart works.
- Heart Failure: A condition where the heart doesn't pump blood as well as it should.
- Heart Valve Diseases: Endocarditis and rheumatic heart disease affect how the valves regulate blood flow in and out of the heart chambers.
- Pericardial Disease: Inflammation of the pericardium or sac that contains your heart.
- Cardiomyopathy: A disease of the heart muscle that makes it harder for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body.
- Congenital Heart Disease: Defects in the heart structure present from birth.
Risk Factors and Statistics
Both modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors influence cardiovascular disease:
- Modifiable Risks: These include lifestyle choices like smoking, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, and excessive alcohol use.
- Non-Modifiable Risks: Age, genetics, and gender are key factors that cannot be changed. Men are generally at higher risk, and the risk increases for everyone as they age.
Prevalence
Recent data highlights the significant impact of cardiovascular disease:
- In the United States, it remains the leading cause of death, accounting for 1 in every 5 deaths. This statistic emphasizes the extensive reach of heart disease across various demographics.
- CVD affects men more frequently and at younger ages than women, but the risk for women increases and approaches that of men as they reach post-menopausal age.
Understanding these various aspects of cardiovascular disease helps recognize its severity and the critical need for comprehensive prevention and management strategies. This foundation sets the stage for exploring how lifestyle interventions like exercise, diet, and stress management play crucial roles in combating this pervasive health challenge.
For more detailed statistics and guidelines, visit CDC Heart
Disease
Facts and the American Heart
Association.
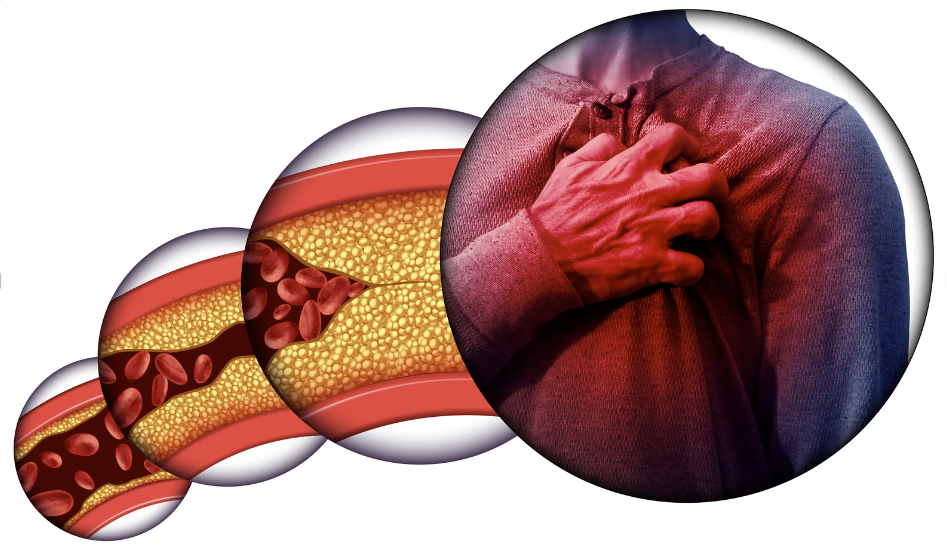
The Emotional Toll of Cardiovascular Disease
The journey through CVD is not solely a physical one. It carries with it profound mental and emotional impacts, touching the lives of not just those diagnosed but also their families and friends. Living with or being at risk for heart disease can evoke a complex tapestry of feelings, from fear and anxiety to a persistent sense of vulnerability.
Imagine the life of John, a 58-year-old who has just been diagnosed with coronary artery disease. The news comes as a shock, disrupting his day-to-day life and replacing it with a nightly struggle against the fear of a heart attack. A haunting awareness of his heartbeats now punctuates his days, each irregular rhythm sending a wave of panic through his already burdened mind.
This emotional upheaval extends to his family, who watch him closely, their lives now revolving around hospital visits, medications, and the constant worry of what might happen if they're not paying attention. Each decision, from meal preparations to outings, is now made with John's heart condition in mind, drastically altering the family dynamics.
Amid these challenges, the role of exercise emerges as a beacon of hope. Engaging in regular physical activity becomes not just a strategy for the physical management of CVD but a therapeutic endeavor. For John, walking every morning has become a ritual; each step is a reaffirmation of life, a moment of triumph over his fears. This routine not only helps to stabilize his physical condition but also provides a mental escape from the confines of his anxieties.
With its myriad benefits, exercise plays a critical role in alleviating the mental strain associated with cardiovascular disease. As we explore the role of physical activity in preventing and managing heart disease, it's crucial to recognize its capacity to mend not just the body but also the spirit.
In the next section, we will explore how specific exercises and fitness routines can help fortify the body against cardiovascular disease, detailing practical steps that can be integrated into everyday life to enhance physical and emotional well-being.
The Role of Exercise in Prevention
Embracing regular exercise is crucial for managing cardiovascular health by strengthening the heart and improving lung capacity. Physical activity enhances the cardiovascular system's efficiency through several key physiological changes:
- Improved Circulation: Regular exercise boosts blood flow, which helps reduce the risk of heart diseases by lowering blood pressure and improving heart function.
- Enhanced Cardiovascular Efficiency: Exercise increases heart rate and stroke volume (the amount of blood pumped per heartbeat). This, in turn, improves blood oxygenation, which is crucial for the health of all body tissues.
- Increased Hemoglobin and Red Cell Mass: Physical activity stimulates hormones that help produce more hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Increased red cell mass allows the body to transport oxygen more efficiently, supporting higher energy levels and better overall health.
These improvements directly reduce the risk of heart disease and enhance longevity and quality of life.
Exercise Recommendations
Health organizations such as the American Heart Association recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity each week. Additionally, the AHA advises engaging in moderate- to high-intensity strength training twice weekly.
Understanding the intensity of exercise is crucial for effective cardiovascular health management.
Here's how to gauge exercise intensity through physiological signals, ensuring you're working within the correct zone for your health goals according to the American Heart Association's guidelines:
- Moderate-Intensity Exercise: This level of intensity increases your heart rate and breathing but doesn't leave you out of breath. You should be able to talk but not sing the words to your favorite song. Physiologically, you work at about 50-70% of your maximum heart rate. Examples include brisk walking, gentle cycling, or water aerobics.
- Vigorous/High-Intensity Exercise: At this level, your breathing is deep and rapid; you can't say more than a few words without pausing for breath. You work at 70-85% of your maximum heart rate, significantly enhancing cardiorespiratory fitness. Activities like running, swimming laps, or cycling fast are typical examples of vigorous-intensity exercise.
These guidelines help ensure that individuals exercise at an intensity that maximizes cardiovascular benefits while minimizing risks, especially important for those new to regular physical activity or those with existing health concerns. Finding a balance that challenges your body but also allows for recovery and adaptation is essential.

Types of Exercise for Cardiovascular Health
Aerobic Exercises
Colloquially known as cardio, aerobic exercise is essential for improving cardiovascular health. Here are some activities categorized based on environment and social setting:
- Indoor Activities:
- Treadmill walking or running: Convenient and unaffected by weather.
- Stationary cycling: Excellent for a low-impact joint workout.
- Aerobics classes: Provides a guided exercise in a social setting.
- Outdoor Activities:
- Jogging or running: Engages more muscles, enhancing cardiovascular endurance.
- Cycling: Builds leg strength and endurance.
- Group sports: Offers aerobic benefits along with social interaction.
- Solo Activities:
- Swimming: Provides a full-body workout that is excellent for the joints.
- Rowing: Offers intensive full-body cardiovascular conditioning.
- Group Activities:
- Dance classes: A fun way to burn calories and improve heart health.
- Hiking groups: Combines physical activity with the therapeutic effects of nature.
Comprehensive Benefits of Aerobic Exercises
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: Regular aerobic activity strengthens the heart muscle, supports proper blood circulation, and decreases the risk of heart disease.
- Enhanced Respiratory Function: Increases lung capacity and efficiency in using oxygen.
- Weight Management: Helps burn calories and control body weight, reducing strain on the heart.

Strength Training
Strength training is crucial for overall fitness and supports heart health. Here's a breakdown of the benefits and examples of different modalities:
- Free Weights:
- Benefits: Enhances muscle strength, improves joint stability, and can be customized for any skill level.
- Examples:
- Barbells: Ideal for heavy lifting targeting large muscle groups.
- Dumbbells: Allow for a range of movements targeting specific muscles.
- Kettlebells: Provide dynamic movement, enhancing cardiovascular fitness.
- Machines:
- Benefits: It offers stability, helps focus effort on particular muscles, and is excellent for beginners.
- Examples: Leg press, chest press, and shoulder press machines.
- Resistance Bands
- Benefits: Provide variable resistance, are portable, and suitable for all levels.
- Examples: Tube bands for bicep curls and loop bands for squats.
- Body-Weight Exercises:
- Benefits: It can be performed anywhere, improving functional strength, balance, and flexibility.
- Examples: Push-ups, pull-ups, squats.
- Suspension Cables:
- Benefits: Increase core stability and enhance muscular endurance.
- Examples: TRX rows, single-leg squats.
Comprehensive Benefits of Strength Training
Strength training improves muscle mass and bone density and aids cardiovascular health by improving metabolic rate and reducing blood pressure. Integrating strength training with aerobic exercises provides a holistic approach that enhances overall cardiovascular function and health, adding variety to exercise routines and maintaining motivation. Combining different forms of exercise ensures a balanced workout regimen that maximizes cardiovascular benefits and caters to personal preferences and fitness goals.

Impact of Exercise on Heart Health
Improving Muscular Fitness:
Strength training boosts lean muscle mass, which in turn enhances metabolic rate. A higher metabolic rate improves energy efficiency and overall health, aiding in managing weight and metabolic conditions linked to heart health. Additionally, stronger muscles contribute to better glucose metabolism, which is crucial for preventing or controlling diabetes and a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Enhancing Cardiovascular Efficiency:
Both endurance and resistance training contribute to a more efficient cardiovascular system. Regular aerobic exercise such as running, cycling, or swimming increases the heart's pumping capacity and the elasticity of blood vessels, improving blood flow and lowering blood pressure. Resistance training complements this by enhancing vascular function and increasing the heart's stroke volume, which is the amount of blood pumped per beat.
Boosting Hemodynamic Response:
Exercise improves the heart's response to and recovery from physical stress. This hemodynamic response includes increased heart rate variability and reduced resting heart rate, indicators of a healthy heart and autonomic nervous system.
Improving Lipid Profiles:
Regular physical activity helps lower harmful LDL cholesterol and triglycerides levels while boosting protective HDL cholesterol. This balance is vital for preventing atherosclerosis, a significant cause of heart attacks and strokes.
Reducing Stress:
Flexibility and balance exercises like yoga significantly impact stress management, thanks to the breathing techniques and mindfulness practiced during these activities. Managing stress is crucial as it directly affects heart health by influencing heart rate, blood pressure, and cortisol levels. Activities such as tai chi and pilates also promote mental relaxation and physical stability, reducing stress and improving cardiovascular health.
The multifaceted benefits of regular exercise encompass not just physical improvements but also significant enhancements in metabolic and mental health, all of which contribute to a robust cardiovascular system. A balanced regimen that includes aerobic, resistance, and flexibility training ensures comprehensive health benefits, fortifying the heart against disease and improving overall quality of life.

Influence of Sleep and Stress on Cardiovascular Health
The Role of Sleep in Heart Health
Sleep plays a critical role in maintaining cardiovascular health. Adequate sleep is essential for the heart to function correctly. It helps to regulate the body's stress hormones, maintain blood pressure, and prevent heart disease. Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, and irregular heartbeat.
- Sleep Duration and Quality: Adults should aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Poor sleep quality and disorders like sleep apnea can lead to higher levels of stress hormones, increased heart rate, and inflammation, all of which are risk factors for heart disease.
- Restorative Effects: During deep sleep, the body enters a state of recovery, which is crucial for heart health. This phase helps repair the heart and blood vessels, ensuring they function optimally.
Stress and Cardiovascular Health
Stress is a known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Chronic stress affects the heart in multiple ways:
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Prolonged stress leads to continuous releases of adrenaline and cortisol, hormones that increase heart rate and blood pressure, straining the cardiovascular system.
- Behavioral Impacts: High-stress levels often lead to unhealthy behaviors such as poor dietary choices, smoking, and sedentary lifestyles, which further deteriorate heart health.
- Direct Impact on Heart Structures: Chronic stress can cause changes in the way blood clots, which increases the risk of heart attacks.
Managing Sleep and Stress for Heart Health
Improving sleep hygiene and managing stress are vital for cardiovascular health. Strategies include:
- Regular Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends, helps regulate your body's internal clock and improves sleep quality.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Regular physical activity, mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises effectively reduce stress and its impact on cardiovascular health.
Integrating these practices into daily life improves cardiovascular health and enhances overall well-being and quality of life. The synergy between adequate sleep, effective stress management, and cardiovascular health cannot be overstated; each element supports and enhances the others, creating a foundation for a healthier heart.

Nutritional Strategies for Cardiovascular Health
Adopting a heart-healthy eating pattern is crucial for preventing and managing cardiovascular disease. This approach focuses on consuming various nutrient-dense foods that support heart function and overall health.
Critical Components of a Heart-Healthy Eating Pattern:
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains like oats, quinoa, and whole wheat over refined grains. They help maintain healthy blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Fruits and Vegetables: These are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Aim for a variety of colors and types to ensure a broad range of nutrients.
- Lean Proteins: Include sources like fish, poultry, legumes, and nuts. Fish such as salmon and mackerel are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
- Healthy Fats: Focus on consuming fats that help maintain healthy cholesterol levels, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- Limited Sodium: Reducing sodium intake is crucial for heart health as high sodium levels can lead to high blood pressure, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Avoiding Harmful Nutrients:
- Trans Fats and Saturated Fats: Limiting these fats is vital as they can raise bad cholesterol levels (HDL) and increase the risk of coronary artery disease.
- Added Sugars: Excessive sugar intake can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of heart disease. It's advisable to minimize foods and beverages with high added sugars.
Practical Tips for Implementing Heart-Healthy Eating Habits:
- Meal Planning: Plan meals incorporating these heart-healthy foods to support your cardiovascular health consistently.
- Mindful Eating: Be aware of portion sizes and eat more slowly to help with digestion and weight management.
- Regular Hydration: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day supports overall metabolic health, which benefits the heart.
Embracing these nutritional strategies can significantly improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease. It's about making smarter food choices that nourish your body and protect your heart.

Royal Blue Fitness: A Holistic Approach to Cardiovascular Health
At Royal Blue Fitness, we recognize the profound impact of CVD on physical health and mental and emotional well-being. We understand that dealing with or being at risk for heart disease can be a significant emotional burden for individuals and their families. Our commitment is to provide a supportive, empathetic environment where every client feels understood and valued.
Our approach goes beyond typical fitness regimes. We offer a comprehensive program tailored to meet the needs of those dealing with cardiovascular health concerns or those aiming to prevent heart disease. Recognizing the mental and emotional aspects of living with or preventing heart disease, we provide support that addresses these dimensions, ensuring that our clients feel supported holistically.
We design fitness programs incorporating cardiovascular training, strength training, and flexibility workouts. Each regimen is tailored to improve heart health and enhance overall endurance while also being fun and engaging to ensure it fits all ages and fitness levels.
We integrate nutrition counseling and stress management into our programs, providing a balanced approach that includes heart-healthy eating habits and effective stress reduction techniques. We aim to empower clients to improve their cardiovascular health and adopt a healthier lifestyle overall in a welcoming and supportive environment.
Our facility is designed to be welcoming and inclusive, providing an atmosphere where all clients, regardless of age or fitness level, feel comfortable and motivated. Our staff is trained in fitness and health management and dedicated to creating a supportive community where every individual's health journey is respected and encouraged.
By choosing Royal Blue Fitness, you are not just attending a gym; you are joining a community that cares deeply about your health and well-being. Together, we work towards lasting improvements in cardiovascular health and overall quality of life.

Conclusion: Commitment to Heart Health
In this comprehensive guide, we've explored the critical elements of cardiovascular wellness, emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach to preventing and managing heart disease. From understanding the complexities of cardiovascular conditions to implementing lifestyle changes that bolster heart health, the journey to a healthier heart is multifaceted.
Regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and effective stress management enhance cardiovascular health. At Royal Blue Fitness, we are dedicated to supporting our clients through customized fitness programs that are effective, enjoyable, and suited to all fitness levels. Our holistic approach extends beyond physical workouts to include nutrition counseling and stress reduction techniques, ensuring that every aspect of heart health is addressed.
By embracing these strategies, individuals can significantly improve their heart function, reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and enhance their overall quality of life. Royal Blue Fitness is committed to being your partner in this journey, providing the support, expertise, and care needed to achieve and maintain optimal heart health. Together, we can take meaningful steps towards a heart-healthy lifestyle, ensuring a brighter, healthier future.
Resources for Cardiovascular Health
For further information and guidance on maintaining cardiovascular health, the following resources from reputable organizations are invaluable:
- American Heart Association (AHA): Provides comprehensive information on heart disease prevention, including detailed guidelines on exercise, nutrition, and overall heart health management. Visit AHA
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Offers extensive data on cardiovascular disease, including statistics on prevalence, risk factors, and preventive measures. Visit CDC
- World Health Organization (WHO): Shares global insights on cardiovascular diseases, including strategies for prevention and management at the international level. Visit WHO
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): Provides heart disease resources and educational materials focusing on lifestyle changes for improving heart health. Visit NHLBI
These resources offer reliable and up-to-date information to help you better understand cardiovascular health and take actionable steps toward a healthier heart.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter and posts
Thank you for Subscribing.
Please try again later.


Business Hours
- Mon - Fri
- -
- Sat - Sun
- -
(925) 318-1310
2001 Contra Costa Blvd Suite A10, Pleasant Hill, CA 94523.
info@royalbluefitness.com
All Rights Reserved | Royal Blue Fitness
